문제 링크: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/23291
23291번: 어항 정리
마법사 상어는 그동안 배운 마법을 이용해 어항을 정리하려고 한다. 어항은 정육면체 모양이고, 한 변의 길이는 모두 1이다. 상어가 가지고 있는 어항은 N개이고, 가장 처음에 어항은 일렬로 바
www.acmicpc.net
<문제 풀이> 구현
0. 어항 표현
N*N 배열을 만들고 N행을 어항의 맨 밑바닥으로 표현했습니다.
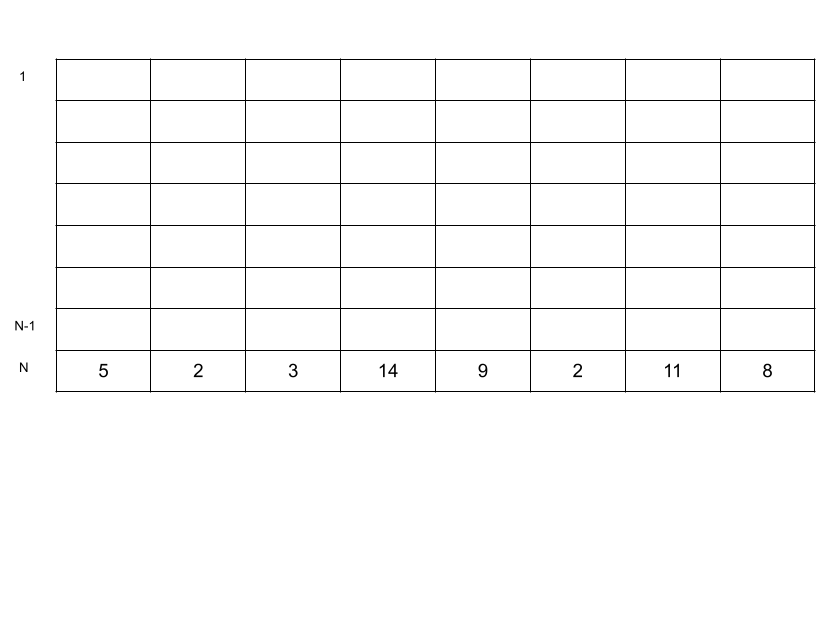
1. 물고기의 수가 가장 적은 어항에 물고기 한 마리 넣는다. 여러 개라면 모두에 한 마리씩 넣는다.
N행에 있는 원소들을 모두 순회하면서 최솟값을 찾으면 됩니다. 최솟값이 여러 개인 물고기를 모두 찾기 위해서 vector에 저장했습니다.
// 1. 물고기의 수가 가장 적은 어항에 물고기 한 마리 넣는다.
// 여러개라면 모두에 한 마리씩 넣는다.
void putFish() {
vector<int> temp;
int minValue = 1e9;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i] < minValue) {
minValue = board[n][i];
temp = {};
temp.push_back(i);
}
else if (board[n][i] == minValue) {
temp.push_back(i);
}
}
for (auto index : temp) {
board[n][index]++; // 물고기를 한 마리씩 넣는다.
}
}2. 어항을 쌓는다.
1) 먼저, 가장 왼쪽에 있는 어항을 그 오른쪽에 있는 어항의 위에 올려놓는다,
N행 1열에 있는 원소를 N - 1행 1열에 저장하고 N행을 왼쪽으로 한 칸씩 이동시키면 됩니다.
2) 2개 이상 쌓여있는 어항을 공중부양 시킨다.
2개 이상 쌓여있는 어항은 직사각형입니다. 이 직사각형을 다른 배열에 저장하면 공중 부양 시킨 것과 같은 효과를 낼 수 있습니다. 먼저 직사각형의 시작점과 끝점의 좌표를 먼저 구합니다.
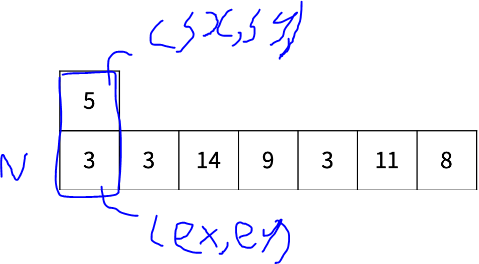
먼저 시작 sx 행은 N행 1열부터 1행 1열까지 순회하면서 처음으로 0인 값이 나오는 행을 찾습니다.
0인 값이 나온 행 바로 이전 행이 시작 sx행이 됩니다.
(시작 sy 열은 항상 1)
그다음 끝 sy 열을 찾기 위해서 sx 행을 기준으로 1열부터 N열까지 순회하면서 처음으로 0인 값이 나오는 열을 찾습니다.
0인 값이 나온 열 바로 이전 열이 끝 ey열이 됩니다.
(끝 ex 열은 항상 n)
공중 부양시킬 직사각형의 시작점과 끝점을 가지고 직사각형을 저장할 배열을 하나 만들어서 저장해 줍니다. 배열에 저장한 것은 직사각형을 공중 부양 시킨 것과 같은 효과가 있습니다.
공중 부양 시킨 다음 어항을 회전하기 전에 한 가지 체크해야 할 게 있는데 회전을 했을 때 맨 밑바닥에 어항이 항상 있어야 합니다.
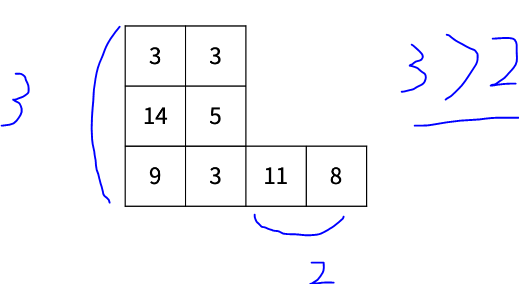
위 그림에서 공중 부양시킬 직사각형의 세로의 길이가, 공중 부양 시키고 난 다음 왼쪽으로 이동시킬 밑바닥의 길이보다 크면 회전을 했을 때 맨 밑바닥에 어항 없는 경우가 생깁니다.
따라서 이 경우에 회전을 진행하지 않도록 해주어야 합니다.
3) N행에 있는 배열을 맨 왼쪽으로 밀어 넣는다.
직사각형을 공중 부양시켰으면(배열에 저장했으면) N행에 있는 배열을 맨 왼쪽으로 밀어 넣으면 됩니다.
4) 공중 부양 배열을 90도 회전시킨다.
저장한 직사각형 배열을 90도 회전시킵니다.
5) 회전시킨 배열을 N - 1행에 쌓는다.
회전시킨 배열의 가장 밑에서부터 하나씩 순회하면서 N-1행부터 차곡차곡 쌓으면 됩니다.
// 2. 어항을 쌓는다.
void rotate() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
tempLevitation[i][j] = levitation[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
levitation[j][n - i] = tempLevitation[i][j];;
}
}
}
void pile() {
// 먼저, 가장 왼쪽에 있는 어항을 그 오른쪽에 있는 어항의 위에 올려 놓는다.
board[n - 1][1] = board[n][1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
board[n][i - 1] = board[n][i]; // N행을 왼쪽으로 한 칸씩 이동
board[n][i] = 0;
}
// 2개 이상 쌓여있는 어항을 공중부양 시킨다.
int sx = 1, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = 1;
while (true) {
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
if (board[i][1] == 0) {
sx = i + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[sx][i] == 0) {
ey = i - 1;
break;
}
}
int bottomCnt = 0;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
bottomCnt++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
if (ex - sx + 1 > bottomCnt) break; // 공중 부양 시킨 배열의 세로 길이가 맨 바닥의 길이보다 크면 더 이상 회전 X
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
// 배열의 맨 밑바닥을 맨 왼쪽으로 밀어 넣는다.
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate(); // 공중 부양 배열을 90도 회전시킨다.
int row = n - 1; // 회전시킨 공중 부양 배열을 한 칸 위에 쌓는다.
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
}
3. 어항에 있는 물고기의 수를 조절한다.
물고기의 수 조절은 단순히 각 칸에 대해서 남, 동 방향으로 조절하면 됩니다. 동, 서, 남, 북을 모두 하지 않는 이유는 한 번 조절한 두 칸 사이에는 물고기의 수를 다시 조절하면 안 되기 때문입니다. 남, 동 방향으로만 물고기의 수를 조절하면 중복 없이 인접한 칸에 대해서 물고기의 수를 조절을 할 수 있습니다.
한 가지 주의할 점은 물고기의 수는 동시에 조절되기 때문에 임시 변수에 저장해 두었다가 실제 배열에 반영해야 합니다.
// 3. 어항에 있는 물고기의 수를 조절한다.
bool check(int x, int y) {
return !(x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > n || board[x][y] == 0);
}
void adjust() {
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) continue;
if (check(i + 1, j)) {
int d = abs(board[i][j] - board[i + 1][j]) / 5;
if (d > 0 && board[i][j] > board[i + 1][j]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] -= d;
tempAdjust[i + 1][j] += d;
}
else if (d > 0 && board[i][j] < board[i + 1][j]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] += d;
tempAdjust[i + 1][j] -= d;
}
}
if (check(i, j + 1)) {
int d = abs(board[i][j] - board[i][j + 1]) / 5;
if (d > 0 && board[i][j] > board[i][j + 1]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] -= d;
tempAdjust[i][j + 1] += d;
}
else if (d > 0 && board[i][j] < board[i][j + 1]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] += d;
tempAdjust[i][j + 1] -= d;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
board[i][j] += tempAdjust[i][j];
if (board[i][j] < 0) board[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
4. 이제 다시 어항을 바닥에 일렬로 놓는다.
문제 조건 그대로 구현하면 됩니다.
// 4. 이제 다시 어항을 바닥에 일렬로 놓는다.
void arrange() {
int col = 1;
init();
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) continue;
tempArrange[n][col] = board[i][j];
col++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
board[i][j] = tempArrange[i][j];
}
}
}
5. 새로운 공중 부양
2번에서 만들었던 공중 부양 코드를 참고해서 조금만 수정하면 만들 수 있습니다.
주의할 점 하나는 회전 후 어항을 왼쪽으로 밀어 넣을 때 2번에서는 맨 밑바닥만 하면 됐지만 5번에서는 밀어 넣어야 할 배열이 2개 이상입니다.
// 5. 새로운 공중 부양
void pile2() {
int sx = n, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = n / 2;
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate();
rotate();
int row = n - 1;
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
void pile3() {
int sx = n - 1, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = n / 4;
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n - 1][i]) {
board[n - 1][col] = board[n - 1][i];
board[n - 1][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate();
rotate();
int row = n - 2;
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
<전체 C++소스코드>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
int board[101][101];
int levitation[101][101];
int tempLevitation[101][101];
int tempAdjust[101][101];
int tempArrange[101][101];
void input() {
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> board[n][i];
}
}
void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
tempAdjust[i][j] = 0;
tempArrange[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 1. 물고기의 수가 가장 적은 어항에 물고기 한 마리 넣는다.
// 여러개라면 모두에 한 마리씩 넣는다.
void putFish() {
vector<int> temp;
int minValue = 1e9;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i] < minValue) {
minValue = board[n][i];
temp = {};
temp.push_back(i);
}
else if (board[n][i] == minValue) {
temp.push_back(i);
}
}
for (auto index : temp) {
board[n][index]++; // 물고기를 한 마리씩 넣는다.
}
}
// 2. 어항을 쌓는다.
void rotate() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
tempLevitation[i][j] = levitation[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
levitation[j][n - i] = tempLevitation[i][j];;
}
}
}
void pile() {
// 먼저, 가장 왼쪽에 있는 어항을 그 오른쪽에 있는 어항의 위에 올려 놓는다.
board[n - 1][1] = board[n][1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
board[n][i - 1] = board[n][i]; // N행을 왼쪽으로 한 칸씩 이동
board[n][i] = 0;
}
// 2개 이상 쌓여있는 어항을 공중부양 시킨다.
int sx = 1, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = 1;
while (true) {
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
if (board[i][1] == 0) {
sx = i + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[sx][i] == 0) {
ey = i - 1;
break;
}
}
int bottomCnt = 0;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
bottomCnt++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
if (ex - sx + 1 > bottomCnt) break; // 공중 부양 시킨 배열의 세로 길이가 맨 바닥의 길이보다 크면 더 이상 회전 X
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
// 배열의 맨 밑바닥을 맨 왼쪽으로 밀어 넣는다.
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate(); // 공중 부양 배열을 90도 회전시킨다.
int row = n - 1; // 회전시킨 공중 부양 배열을 한 칸 위에 쌓는다.
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
}
// 3. 어항에 있는 물고기의 수를 조절한다.
bool check(int x, int y) {
return !(x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > n || board[x][y] == 0);
}
void adjust() {
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) continue;
if (check(i + 1, j)) {
int d = abs(board[i][j] - board[i + 1][j]) / 5;
if (d > 0 && board[i][j] > board[i + 1][j]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] -= d;
tempAdjust[i + 1][j] += d;
}
else if (d > 0 && board[i][j] < board[i + 1][j]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] += d;
tempAdjust[i + 1][j] -= d;
}
}
if (check(i, j + 1)) {
int d = abs(board[i][j] - board[i][j + 1]) / 5;
if (d > 0 && board[i][j] > board[i][j + 1]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] -= d;
tempAdjust[i][j + 1] += d;
}
else if (d > 0 && board[i][j] < board[i][j + 1]) {
tempAdjust[i][j] += d;
tempAdjust[i][j + 1] -= d;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
board[i][j] += tempAdjust[i][j];
if (board[i][j] < 0) board[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 4. 이제 다시 어항을 바닥에 일렬로 놓는다.
void arrange() {
int col = 1;
init();
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) continue;
tempArrange[n][col] = board[i][j];
col++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
board[i][j] = tempArrange[i][j];
}
}
}
// 5. 새로운 공중 부양
void pile2() {
int sx = n, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = n / 2;
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate();
rotate();
int row = n - 1;
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
void pile3() {
int sx = n - 1, sy = 1, ex = n, ey = n / 4;
fill(&levitation[0][0], &levitation[100][101], 0);
for (int i = sx; i <= ex; i++) {
for (int j = sy; j <= ey; j++) {
levitation[i - sx + 1][j - sy + 1] = board[i][j];
}
}
int col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n][i]) {
board[n][col] = board[n][i];
board[n][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
col = 1;
for (int i = ey + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (board[n - 1][i]) {
board[n - 1][col] = board[n - 1][i];
board[n - 1][i] = 0;
col++;
}
}
rotate();
rotate();
int row = n - 2;
col = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (levitation[i][j]) {
board[row][col] = levitation[i][j];
col++;
}
}
if (col > 1) {
col = 1;
row--;
}
}
}
void solve() {
init();
input();
int ans = 0;
while (*max_element(board[n] + 1, board[n] + n + 1) - *min_element(board[n] + 1, board[n] + n + 1) > k) {
putFish();
pile();
adjust();
arrange();
pile2();
pile3();
adjust();
arrange();
ans++;
}
cout << ans;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
cs |
'알고리즘 문제풀이 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 9465번] 스티커 (2) | 2023.04.12 |
|---|---|
| [백준 17626번] Four Squares (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| [백준 21608번] 상어 초등학교 (0) | 2023.04.08 |
| [백준 23289번] 온풍기 안녕! (0) | 2023.04.06 |
| [백준 1938번] 통나무 옮기기 (0) | 2023.04.04 |